
- #HOW TO REPRESENT A CARRY IN DIGITAL WORKS HOW TO#
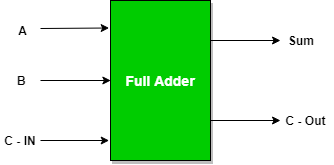
- #HOW TO REPRESENT A CARRY IN DIGITAL WORKS FULL#
#HOW TO REPRESENT A CARRY IN DIGITAL WORKS FULL#
Implementation of Full Subtractor using Half Subtractors –Ģ Half Subtractors and an OR gate is required to implement a Full Subtractor. = A’B’Bin +A’BBin’ + A’BBin + A’BBin + A’BBin + ABBin ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Examīout = A’B’Bin + A’BBin’ + A’BBin + ABBin.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.
 GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys. If anyone has anything to add, please leave a comment. Hope this has given everyone a good overview. better EMC performance and isolation of circuits. easy incorporation of modern electronic CT and VT sensors. improved measurement accuracy and recording of information. interoperability between devices made by different manufacturers. easier and simpler installation (much less wiring). The digital substation offers numerous advantages over a conventional arrangement. Note: current measurement uses the Faraday Effect and voltage measurement uses the Pockels Effect. Optical transducers also tend to be smaller, have improved linear characteristics and more accurately reproduce the primary signal. The transducers are able to measure both current and voltage.Īs the signals are generated and transmitted using optical fibre, transducer signals are not subject to voltage drop issues and electromagnetic interference which can affect conventional equipment. These devices operate by measuring changes in the optical performance of fibres in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. Intelligent Electronic Devices (IDE)Ī growing trend in the digital substation is the use of optical current and voltage transducers (sometimes called non-conventional instrument transformers - NCIT). The digital substations consist of several key components and elements. Compared to the traditional substation where everything is connected together with hundreds of individual copper cables, the advantages become obvious. While the arrangement shown in not the only way to implement a digital substation, it does represent one of the more commonly adopted approaches.īy taking the various elements required of a substation (circuit breakers, protection relays, CTs and VTs, etc.) and interconnecting these using optical fibre, the physical realisation of a substation becomes easier while at the same time, it's reliability and understandability increases. The digital substation is implemented using the elements and components shown in the illustration.
GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys. If anyone has anything to add, please leave a comment. Hope this has given everyone a good overview. better EMC performance and isolation of circuits. easy incorporation of modern electronic CT and VT sensors. improved measurement accuracy and recording of information. interoperability between devices made by different manufacturers. easier and simpler installation (much less wiring). The digital substation offers numerous advantages over a conventional arrangement. Note: current measurement uses the Faraday Effect and voltage measurement uses the Pockels Effect. Optical transducers also tend to be smaller, have improved linear characteristics and more accurately reproduce the primary signal. The transducers are able to measure both current and voltage.Īs the signals are generated and transmitted using optical fibre, transducer signals are not subject to voltage drop issues and electromagnetic interference which can affect conventional equipment. These devices operate by measuring changes in the optical performance of fibres in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. Intelligent Electronic Devices (IDE)Ī growing trend in the digital substation is the use of optical current and voltage transducers (sometimes called non-conventional instrument transformers - NCIT). The digital substations consist of several key components and elements. Compared to the traditional substation where everything is connected together with hundreds of individual copper cables, the advantages become obvious. While the arrangement shown in not the only way to implement a digital substation, it does represent one of the more commonly adopted approaches.īy taking the various elements required of a substation (circuit breakers, protection relays, CTs and VTs, etc.) and interconnecting these using optical fibre, the physical realisation of a substation becomes easier while at the same time, it's reliability and understandability increases. The digital substation is implemented using the elements and components shown in the illustration. #HOW TO REPRESENT A CARRY IN DIGITAL WORKS HOW TO#
Part 10 - provides instruction on how to carry out conformance testing of an IEC 62850 installation.Parts 8 and 9 - identify the required mappings for the station and process bus.Part 7 - provides details on the data models and transactions used by the standard.Part 5 and 6 - detail the communication requirements and language used.Part 4 - project management of products and tenders for an IEC 61850 installation.Parts 1 to 3 - are an overview and guide to understanding the standard, in addition to providing the general rules.The standard has ten parts, and the structure is summarised by the following: It is the backbone and framework around which a digital substation is built.

This is the international standard governing communications, SCADA and automation systems within substations. The digital substation starts with IEC 61850 "Communication networks and systems in substations".
The substation system architecture is dividing into three levels 1) the station level where operations, engineering functions and reporting take place, 2) the bay level where system protection and control functions are implements and 3) the process level where signals from CTs and other transducers are transmitted. In the arrangement, the workstations, protection devices and low level transducers are connected together on an optical fibre communications backbone. The image illustrates the concepts associated with a digital substation.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
